According to the law, all packaged products are required to show nutritional values on the package, box, etc.
So, you need to know how to read and understand the basics of ingredients that impact the health of you and your family.
Not only that, reading food labels and nutrition facts will help you make informed choices about what you and your family eat and drink.
Through food labels you will know the content of nutrients, such as fat, protein, starch, sugar, fiber, sodium, vitamins, minerals, and so on.

Depending on the diet and health status, each person will calculate the above parameters to make the healthy food choices and eat the right amount to provide enough energy for the body and reduce the risk of health problems.
This is especially important for people who are suffering from diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes, etc., who need to follow a healthy and reasonable diet.
I. Nutrition facts on food packaging
The information mentioned about the nutritional index on food packaging includes:
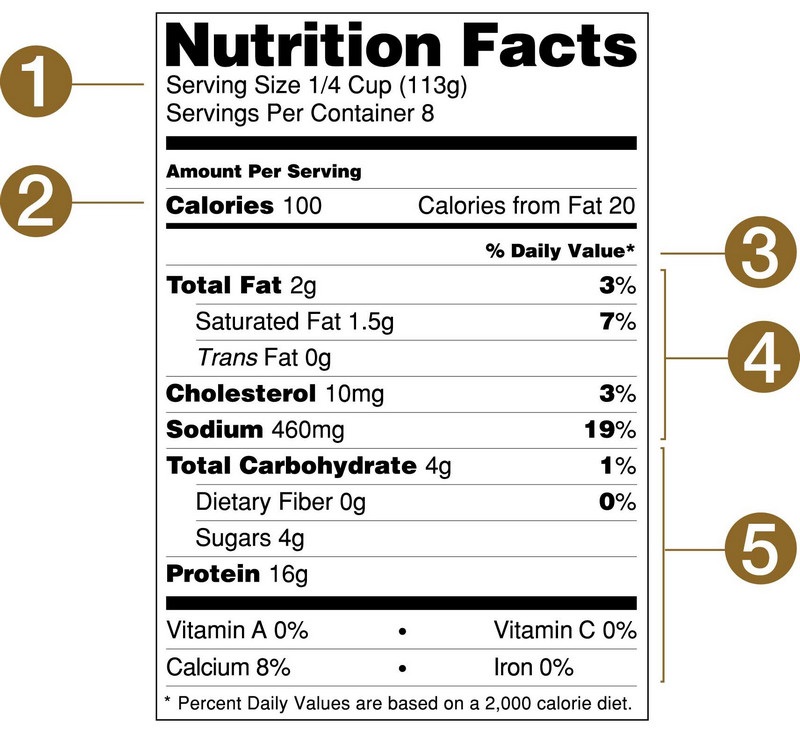
#1. Serving Size
Servings are the first information mentioned in the nutrition facts on the food packaging.
Usually, nutrition labels will list both the standard serving size information and the number of servings in each food package.
Servings are usually standardized in terms of the same units as: grams, milliliters, pieces, etc.
A serving is a standard of food for a person in a day, meeting the needs of nutrients and energy for the body. Serving size has a great influence on the number of calories and the nutritional composition in it.
Therefore, users need to pay attention to the serving size in the food package to avoid consuming too large a serving (equivalent to eating a lot of calories, which can lead to weight gain).
#2. Calories
The calorie information on food packaging shows how much energy the user has consumed from the food.
As per FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulations, calorie information on nutrition labels is usually in large and bold font so that consumers can easily identify them at the outset.
Calories on food labels include 2 values:
- General calories
- Calories derived from fat.
The number of servings determines the number of calories consumed. Paying attention to the calories on food labels will help you control your weight.
About calorie levels in food:
- 40 calories is low
- 100 calories is medium
- 400 calories is high.
As mentioned above, the number of calories you eat will greatly affect your weight. If you consume too many calories per day, it will increase the risk of overweight and obesity.
Therefore, each person needs to control their diet by comparing the calories on food packaging, not consuming more than the limit.
Calculate your daily calorie intake and calorie expenditure, balancing these two indicators will help you manage your weight according to your wishes.
#3. Substances to supplement
On nutrition labels, the substances that need to be supplemented by the body are usually shown in blue.
These substances include Fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium and iron. Eating enough of these substances will help improve health and reduce the risk of many diseases.
Specifically, adequate calcium supplementation helps reduce the risk of osteoporosis; eating enough fiber will promote bowel movements; a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low in saturated fat and cholesterol, etc. helps reduce the risk of heart disease.
#4. Substances to limit
On nutrition labels, substances to be restricted are usually shown in yellow.
These include fats, including saturated and trans fats, cholesterol and sodium, etc. as they can lead to an increased risk of chronic diseases such as heart attack, cancer or high blood pressure, etc.
Therefore, you should limit your fat intake to have a balanced diet and good health.
#5. Percent Daily Value (%DV)
The percent Daily Value (%DV) is usually shown at the bottom of the Nutrition Facts label.
The percent Daily Value (%DV) shows how much a nutrient in a serving of food will be provided when using a standard serving (2,000-calorie per day diet).
Foods that provide 5% DV of a particular nutrient are considered to be low and those that provide 20% DV or more are considered to be high.
NOTE:
The daily value is calculated based on an average diet of 2,000 calories per day. If a person is eating less or more of these calories each day, the percentage of the daily value should be adjusted accordingly.

II. Some notes when reading the nutrition facts on food packaging
When choosing foods, you need to pay extra attention to the date of manufacture and the expiration date on the packaging/label.
The following important notes will help users choose healthy foods:
- Prioritize paying attention to the percentage of Daily Value instead of grams or milliliters.
- Not all nutrition facts listed on food labels are healthy.
- Calorie intake is not required to be 2,000 calories/day as shown on food labels. This also depends on your condition and age.
- It is necessary to regularly monitor the number of servings per day to calculate the value of nutritional ingredients on food labels.
- The nutrition index on food packaging is very important information for each person, especially for those who are on a diet or in the process of treating chronic diseases such as blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, obesity, etc.
[BONUS]
Suggestions on the amount of nutrients that should be consumed daily.
Saturated fat: May increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. An adult should eat no more than 20g of saturated fat per day.
Trans fats: Increases the risk of heart disease. It’s best not to eat trans fats. This substance is often found in fried foods, margarine and snacks.
Cholesterol: Normal healthy people should only eat less than 300mg/day and people with heart disease should only eat less than 200mg/day.
Fiber: Helps the body digest food, reducing the risk of heart disease and diabetes. A food is considered high in fiber if it contains more than 5g of fiber per serving.
Men under 50 should eat at least 38g of fiber per day and women under 50 should eat at least 25g of fiber per day. Fiber is found in fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
Vitamins and minerals: Priority should be given to foods with nutrition labels that mention vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium and iron.
Salt: Healthy people should eat less than 2,300mg of salt/day. People with kidney disease, osteoporosis, a history of high blood pressure and pregnant women should eat less than 1,500mg of salt/day. If you eat a lot of salt, eat more potassium-rich foods like tomatoes, bananas and orange juice to prevent calcium loss.
Sugar: Contains many calories and is not good for health, so choose foods that contain no more than 5g of sugar per serving. People with diabetes need to pay special attention to the information about sugar on food packaging.
We hope you find the information in this article useful!


